You feel a small click during a routine step. The sensation is odd but brief today. Later, a sharp pinch arrives while rising from a chair. A question appears immediately in your mind. Is this a muscle strain or something deeper? The hip labrum often enters the conversation here. Let’s explore the basics with calm and clarity.
What is the hip labrum?
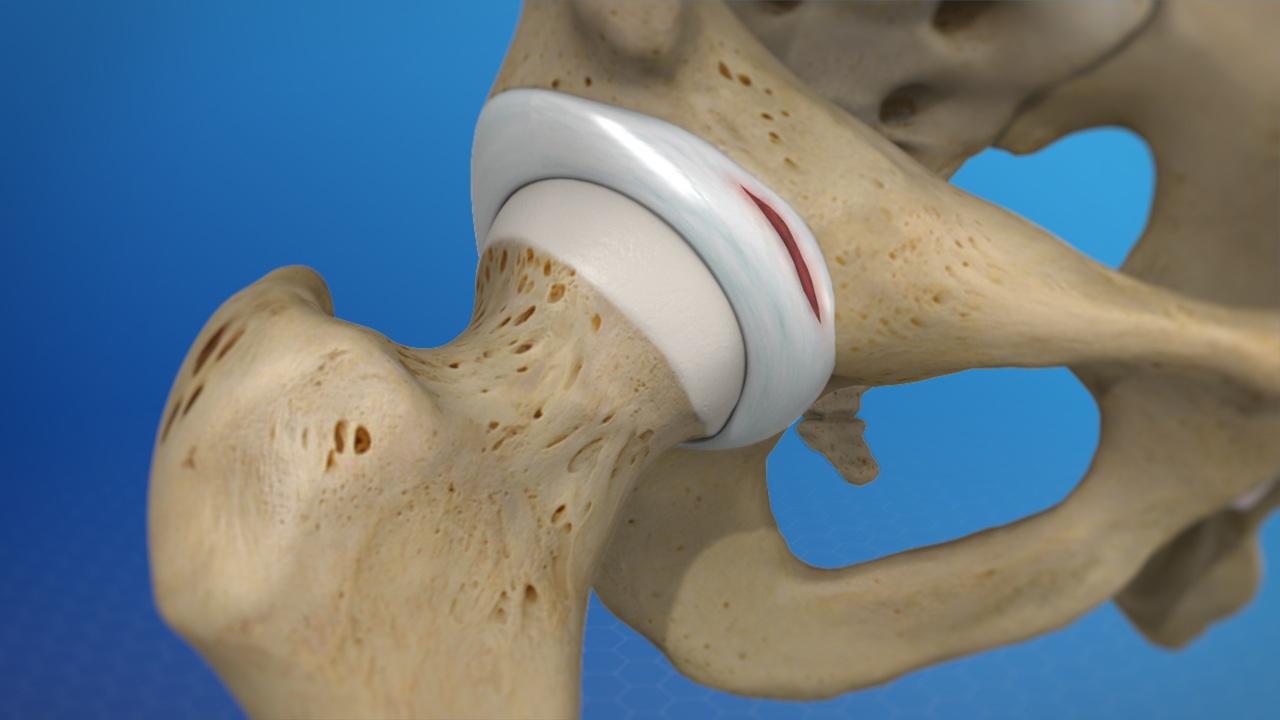
The hip labrum is a ring of fibrocartilage. It rims the socket and deepens the joint. That rim improves stability during daily motion. It also helps maintain joint lubrication and pressure. A healthy labrum feels silent during activity. A torn labrum can feel noisy and sharp.
Why do tears happen?
Tears can follow a clear injury during sport. They can also arise from slow mechanical stress. Subtle alignment differences increase rubbing forces. Repetitive twisting can strain the labral edge. Cartilage ages and loses strength with time. Small weak points then become symptomatic tears.
Which factors raise your risk?
High impact sports increase strain on the rim. Repeated pivoting challenges the joint under load. Work that demands deep squatting adds stress. Prolonged sitting can tighten surrounding tissues. Certain bony shapes limit hip clearance mechanically. Family patterns sometimes reveal similar hip shapes.
How do symptoms usually start?
Many people notice groin centered pain first. Others feel pain at the outer hip region. Clicking or catching sounds can accompany movement. Standing from low chairs can trigger sharp discomfort. Long car rides may leave the joint irritable. Sleep position can suddenly matter every night.
Which movements make pain worse?
Deep flexion often provokes a sharp pinch. Twisting while loaded can trigger catching sensations. Crossing the legs may reproduce familiar pain. Sprinting or bounding magnifies repetitive stress. Sudden direction changes can feel risky immediately. Gentle walking may remain comfortable and steady.
How is a labral tear diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with a detailed conversation first. A physical exam evaluates motion and strength. Specific maneuvers may reproduce characteristic pain. Plain X rays assess bone shapes and spacing. MRI can visualize soft tissues and cartilage layers. Your clinician synthesizes findings into a clear plan.
Do imaging tests always show the tear?
Imaging improves clarity yet remains imperfect sometimes. Small tears can hide within complex structures. Motion pain may outpace pictures occasionally. Findings also include incidental, silent changes sometimes. Clinicians combine images with exam and history always. Treatment targets the person, not a picture alone.
When should you seek care?
Seek care if pain persists beyond several weeks. Call sooner if walking becomes unsteady suddenly. Seek help for night pain that interrupts sleep. Report locking sensations that halt movement abruptly. Early evaluation prevents unnecessary compensations elsewhere. Timely plans reduce frustrating, stop start recovery cycles.
Can simple measures reduce symptoms early?
Yes, many people benefit from basic steps. Reduce deep hip flexion during the first weeks. Choose chairs that allow easier standing transitions. Keep strides shorter during brisk walks outside. Use heat for morning stiffness and comfort. Ice can calm irritation after active periods. Small adjustments protect healing momentum daily.
How does physical therapy help?
Therapy targets strength, control, and mobility together. Glute muscles gain thoughtful attention for support. Core stability reduces unnecessary hip strain daily. Gentle mobility improves available motion without force. Balance drills improve control during direction changes. Programs adapt with your comfort and goals.
What about activity modification today?
Retire deep squats during early phases of care. Replace long hills with flat, steady walks. Choose cycling with higher seats and easy gears. Pause aggressive stretching that forces painful end range. Build stamina with short, frequent sessions initially. Consistency matters more than single heroic efforts.
Do injections have a role here?
Injections can reduce inflammation and pain briefly. Relief can clarify diagnosis when uncertainty remains. Shorter pain windows allow effective strengthening work. Decisions depend on history and clinician guidance. They are not stand alone cures by themselves. Plans still rely on skillful movement training.
When is surgery considered?
Surgery enters the discussion after persistent symptoms. Imaging should match clinical findings carefully. Functional goals should be realistic and clear. Conservative care deserves a fair, consistent trial first. Some tears with mechanical catching demand attention. Surgical decisions remain shared and thoughtful.
What happens during arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy uses small cameras and instruments. Surgeons repair or trim unstable labral tissue. Bone shapes can be reshaped when needed. Procedures aim to restore smoother joint mechanics. Hospital stays are typically brief and focused. Rehab begins quickly with guided, graded movement.
How long does recovery usually take?
Recovery times vary widely across people. Simple strains settle within several weeks. Confirmed tears may require months of work. Surgical recoveries follow staged milestones carefully. Strength and control arrive before powerful moves. Patience and steady practice beat rushed timelines.
Can you return to sport safely?
Yes, many athletes return to desired sports. Programs rebuild movement patterns progressively and thoughtfully. Landing mechanics receive special attention and coaching. Cutting drills come later with close supervision. Sport testing considers strength, control, and confidence. Passing criteria supports safe, joyful returns.
What daily habits protect healing?
Sit on higher chairs during early recovery weeks. Break long sitting with short standing periods. Carry loads with balanced, even hands. Choose supportive, stable footwear for errands. Warm up joints before demanding chores. Respect early signals rather than pushing through.
How should you sleep with hip pain?
Sleep on the non painful side initially. Place a pillow between your knees nightly. This reduces rotation and tension at rest. Back sleeping can also work with support. A small pillow under knees relieves pressure. Good sleep accelerates tissue repair and mood.
Which shoes make a difference today?
Shoes that cushion and stabilize help comfort. Excessively flexible shoes increase strain sometimes. Rotate pairs to vary small daily forces. Keep worn shoes out of heavy use. Insoles can support alignment when advised. Comfort with stability guides practical choices well.
How does posture influence hip stress?
Neutral spine and pelvis reduce labral strain. Prolonged slouching shifts load toward edges. Tall, relaxed posture spreads forces more evenly. Core engagement supports movement without gripping. Small corrections beat dramatic postural efforts. Repeatable positions win across long workdays.
What role does nutrition play in recovery?
Recovery benefits from adequate protein intake. Colorful vegetables support broader nutrient needs. Omega rich foods can support joint comfort. Hydration keeps tissues resilient during activity. Gentle caffeine timing protects sleep and repair. Meals shape energy across rehab sessions.
Can pain management avoid overreliance on pills?
Non drug strategies help many people daily. Heat and ice cycles can calm irritated tissues. Breathing practices reduce muscle guarding around pain. Gentle movement interrupts fear based avoidance loops. Over the counter options may still help briefly. Always discuss dosing and duration with clinicians.
How do comorbidities change the plan?
Back or knee issues can influence hip load. Flat feet may alter forces during walking. Metabolic conditions can slow tissue repair. Sleep disorders reduce recovery quality noticeably. Clinicians integrate these details into programs. Coordination keeps progress steady and realistic.
What myths cause confusion here?
Pain location does not always index damage. Loud clicks do not always mean worsening. Rest alone rarely solves mechanical strain. Stretching harder is not always better. Strong glutes matter beyond aesthetic goals. Smart practice beats random exercises every time.
How do you talk with your clinician clearly?
Describe pain location with familiar hand cues. Explain movements that reproduce symptoms reliably. Share workplace and sport demands honestly. Note any night pain or morning stiffness. Ask how progress will be measured practically. Agree on a timeline for reassessment together.
Where do braces and supports fit?
Some people benefit from soft supports briefly. Supports remind the body to move thoughtfully. They are not permanent solutions by themselves. Overreliance can weaken helpful stabilizers gradually. Use them during specific demanding tasks only. Remove them as control and confidence return.
How do workplace setups affect recovery?
Desk height and chair angle matter daily. Hips should sit slightly higher than knees. Feet should rest flat and steady always. Stand and stretch at predictable intervals. Short hallway walks refresh joints and focus. Simple setups save many quiet aches.
What about driving and long trips?
Plan breaks for brief standing and walking. Adjust seat height to reduce deep hip flexion. Use a small lumbar support when helpful. Keep wallet and phones out of back pockets. Heat settings can soothe during cold weather. Long trips deserve extra recovery time afterward.
How does stress shape symptoms?
Stress tightens muscles without your permission. Guarding increases joint compression subtly. Breathing practices reduce that hidden load. Short nature walks can lower tension quickly. Good sleep lowers sensitivity to daily irritants. Calm minds move with better coordination.
When do children and teens face labral tears?
Young athletes meet high training volumes sometimes. Repetitive drills can exceed tissue readiness. Growth phases change mechanics and strength quickly. Early coaching on landing and cutting helps. Rest days protect bodies during growth spurts. Family support keeps plans sustainable and kind.
How does aging affect the labrum?
Aging changes collagen quality gradually. Small frays can accumulate over years. Surrounding muscles also lose strength without training. Gentle resistance work protects joint mechanics effectively. Balance training reduces falls and awkward twists. Aging bodies still learn and adapt well.
What is femoroacetabular impingement exactly?
It describes contact between femur and socket. Certain shapes narrow joint clearance during motion. Repeated contact can irritate the labrum over time. Therapy improves motion strategies and strength. Surgery can reshape bone when necessary later. Decisions depend on symptoms and goals.
How do clinicians measure progress meaningfully?
They track pain during specific daily tasks. They measure range with simple, repeatable positions. Strength testing focuses on glutes and core. Balance and control receive graded challenges regularly. Milestones include stairs, car rides, and sleep. Progress is functional, not only numerical charts.
What can runners adjust quickly?
Shorten stride to reduce braking forces. Increase cadence slightly for smoother loading. Choose flatter routes during early phases. Alternate running days with strength days. Warm up with marching and light drills. Rebuild distance after comfort becomes consistent.
Where does cycling fit into rehab?
Cycling allows rhythmic motion with control. Raise the seat to limit deep flexion. Start with shorter, low resistance sessions. Monitor symptoms for delayed irritation later. Combine cycling with targeted strength work. Variety protects tissues from repetitive overload.
Should you stretch tight hip flexors daily?
Gentle stretching can help when controlled. Avoid aggressive end range tension early. Pair stretches with glute activation afterward. Strength balances newfound flexibility effectively. Consistency matters more than intensity here. Minutes daily beat occasional heroic sessions.
According to our editor’s research, what helps?
According to our editor’s research, small anchors work best. People who stand each hour recover faster. Walkers who shorten strides report fewer flares. Households that raise chair heights move easier. Patients who journal triggers understand patterns sooner. Simple tools beat complex, forgotten plans.
As a result of our editor’s reviews, what works weekly?
As a result of our editor’s reviews, structure wins. A fixed therapy schedule prevents gaps easily. A Sunday prep sets clothing and bands ready. A midweek check refines goals with clarity. A Friday walk gauges stamina and mood. These rhythms keep progress visible and motivating.
Which red flags need urgent evaluation?
Seek urgent care for sudden severe pain. Report new weakness after an audible pop. Call immediately for fever and joint redness. Report leg numbness or loss of control. Do not ignore night pain with fevers. Timely action protects joint health and safety.
How do official recommendations support decisions?
Orthopedic societies publish careful practice summaries. Sports medicine groups outline graded return strategies. Public health programs promote workplace ergonomics clearly. National health services describe imaging roles responsibly. These guidance sources align with clinic experience. They help households plan with confidence.