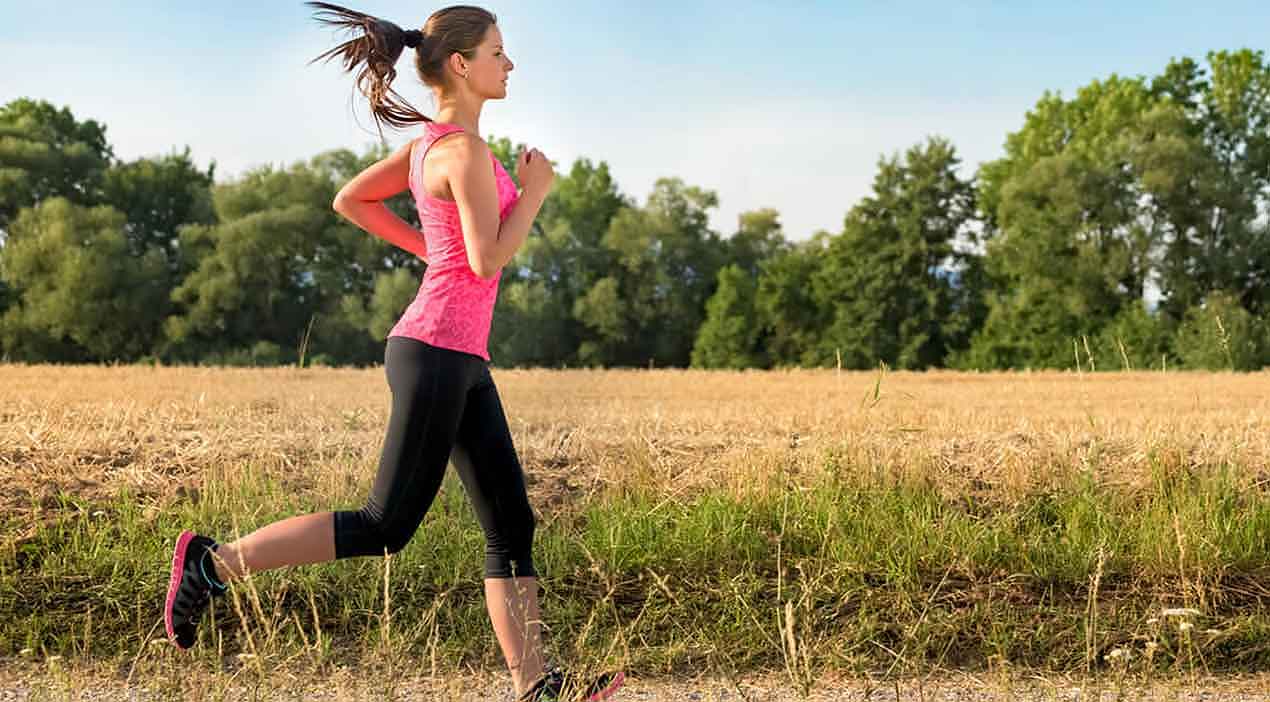
Have you ever gone out for a light run only to feel an unexpected twinge the next morning? Many runners describe this moment as confusing because the discomfort often appears without a clear cause. According to our editor’s research, most running injuries begin long before pain becomes noticeable. Small habits, posture changes, and repetitive stress quietly build tension across the legs. When these tensions accumulate, the body eventually signals distress through soreness or swelling. Understanding these patterns helps runners avoid frustration and keep their training safe and enjoyable.
Why do running injuries appear so suddenly?
Running injuries seem sudden because underlying issues build gradually beneath the surface. These problems rarely start with sharp pain but instead with subtle tissue stress. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many orthopedic specialists emphasize that repetitive load affects muscles and joints quietly. The body tries to compensate for weak areas, creating new movement patterns that increase pressure. When these compensations continue long enough, discomfort finally becomes noticeable. This delayed awareness often surprises runners who believed their form was completely fine. Recognizing early signs can help prevent injuries before they become limiting.
How does improper footwear increase injury risk?
Improper footwear increases risk because each step depends on adequate support and stability. Shoes with poor cushioning force joints to absorb repetitive impact. According to our editor’s research, orthopedic professionals frequently identify outdated or unsuitable shoes as a primary cause of running pain. The wrong shoe also alters foot alignment, affecting knees and hips in a chain reaction. Runners often underestimate how quickly footwear materials lose structural integrity. When support fades, small imbalances turn into repeated strain on soft tissues. Choosing appropriate shoes improves comfort and reduces stress on the entire leg.
Why does overtraining create common running injuries?
Overtraining creates injuries because muscles need time to rebuild after every workout. When runners push too frequently, the body enters a state of cumulative fatigue. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many sports physicians confirm that fatigue weakens stability during movement. Weak stability then increases the likelihood of missteps and uneven loading across joints. Overtraining also elevates inflammation, making tissues more vulnerable to strain. Without strategic rest, even moderate workouts can lead to persistent pain. Preventing overtraining requires listening to signals of fatigue before they escalate.
What causes shin splints and how are they managed?
Shin splints develop when repeated stress irritates tissues along the front of the lower leg. This irritation often comes from sudden increases in training volume or hard running surfaces. According to our editor’s research, many orthopedists recommend modifying intensity rather than stopping activity entirely. Ice, rest, and gentle stretching help reduce irritation during early stages. Injury prevention also depends on strengthening muscles around the shin to improve overall stability. Once stability improves, running becomes smoother and less painful. Gradual progression helps runners avoid repeated flare ups.
How does plantar fasciitis develop in runners?
Plantar fasciitis develops when the thick band beneath the foot becomes strained. Running on tight calves or weak arches increases pressure on this structure. As a result of our editor’s reviews, sports clinicians note that morning heel pain is the most recognizable symptom. The condition worsens when runners ignore early stiffness and continue training at full intensity. Supportive footwear and targeted stretching reduce strain on the fascia. Strengthening the foot’s intrinsic muscles also improves gait stability. With consistent care, discomfort usually decreases significantly over time.
Why do runners frequently experience IT band discomfort?
Runners frequently experience IT band discomfort because this long connective tissue absorbs considerable lateral stress. Poor hip stability and weak gluteal muscles increase tension along the IT band. According to our editor’s research, many orthopedic assessments reveal that imbalance, not mileage, triggers this issue. When the hip rotates improperly, the IT band compensates and becomes irritated. Foam rolling and stretching help reduce short term tightness, but long term improvement requires stronger hip support. Balanced muscle groups allow smoother movement across the knee. This harmony reduces friction and improves overall comfort.
What leads to Achilles tendon irritation during running?
Achilles tendon irritation develops when calf muscles tighten or when sudden training changes overload the tendon. The tendon receives limited blood flow, which makes recovery slower than other tissues. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many doctors advise avoiding quick jumps in running intensity. Tight calves increase tension on the Achilles, creating microtears that cause pain. Strengthening and gentle eccentric exercises support healing and prevent relapse. Supportive training habits help maintain comfortable movement. Listening to early stiffness prevents more serious tendon problems.
Why does weak core strength contribute to leg injuries?
Weak core strength contributes to leg injuries because the core stabilizes posture during every step. When the core weakens, the legs absorb additional stress to compensate. According to our editor’s research, imbalanced strength increases rotational forces around the hips. These forces disrupt alignment and increase the likelihood of knee discomfort. A strong core supports smoother strides and reduces unnecessary swaying motions. Improved stability also helps maintain balance during long runs. Consistent core work helps protect joints from repetitive strain.
How does running form influence injury risk?
Running form influences injury risk because small alignment issues multiply across thousands of steps. Leaning too far forward increases pressure on the knees, while overstriding strains the hamstrings. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many coaches recommend shorter strides for safer movement. Shorter strides reduce impact and support smoother foot landings. Improving form reduces energy waste and enhances comfort during longer runs. Even minor adjustments create meaningful long term benefits. Awareness of form protects the body from preventable stress.
Why is recovery essential for injury prevention?
Recovery is essential because tissues require time to repair microscopic damage caused by running. Adequate sleep and rest restore energy levels and reduce inflammation. According to our editor’s research, recovery days help prevent long term wear on joints. Gentle movement like walking or light stretching supports circulation during rest. This circulation brings nutrients that support tissue healing. Without recovery, injuries become more frequent and harder to treat. Consistent rest promotes stronger and more resilient movement patterns.
How can orthopedics support injured runners?
Orthopedics supports injured runners by identifying the root cause rather than just treating symptoms. Specialists analyze gait mechanics and muscle imbalances to design targeted care plans. As a result of our editor’s reviews, orthopedic assessments often reveal correctable posture issues. Customized exercises help strengthen weak areas that contribute to discomfort. Bracing or taping may support healing in early stages. Orthopedic care also guides runners on safe progression back to training. Professional guidance helps prevent recurring injuries.
What orthobiologic methods assist in recovery?
Orthobiologic methods assist recovery by supporting natural tissue healing. Techniques like platelet concentration or cellular therapies use the body’s resources to improve healing. According to our editor’s research, these methods help reduce inflammation and support long term tissue strength. They are often used when injuries heal slowly or become chronic. Orthobiologic support complements traditional therapy for improved recovery. Many athletes use these methods to extend training longevity. When applied carefully, they encourage more efficient healing.
Why does gradual progress reduce running injuries?
Gradual progress reduces injuries because tissues adapt slowly to new demands. Jumping into intense sessions overwhelms muscles, joints, and tendons. As a result of our editor’s reviews, progressive training remains the safest approach for runners. Slow increases in distance or speed help the body adjust without weakening stability. Gradual progress also improves confidence and reduces fear of injury. Consistency becomes easier when the body feels supported rather than overloaded. This steady approach creates comfort and long term success.Running injuries often emerge quietly because small training habits and unnoticed movement patterns create gradual stress on the soft tissues leading to pain that disrupts progress and reduces motivation
Running injuries often emerge quietly because small training habits and unnoticed movement patterns create gradual stress on the soft tissues leading to pain that disrupts progress and reduces motivation