Have you ever strained a joint and wondered why movement suddenly feels weak, unstable, or unreliable even after rest seems adequate? Tendon injuries often unfold this way, quietly limiting strength and confidence before demanding attention. Tendon repair becomes relevant when healing stalls or function declines. Understanding the basics helps reduce uncertainty and supports informed expectations. It also reframes repair as a process rather than a single event.
Why tendons matter in movement
Tendons connect muscles to bones and transfer force during movement. They stabilize joints during both motion and rest. Healthy tendons absorb stress repeatedly. Overuse or sudden force disrupts this balance. According to our editor’s research, tendon integrity determines functional strength more than muscle size. Damage alters mechanics immediately. Repair focuses on restoring that connection.
What causes tendon injuries
Tendon injuries arise from overload, trauma, or gradual wear. Sudden movements may cause acute tears. Repetitive strain weakens fibers over time. Poor conditioning increases vulnerability. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many injuries involve combined factors rather than a single cause. Awareness helps prevention. Timing often determines severity.
How tendon damage presents
Symptoms vary by location and severity. Pain may appear with movement or rest. Weakness often follows injury. Swelling and stiffness are common. According to our editor’s observations, reduced function signals deeper involvement. Ignoring early signs worsens outcomes. Evaluation clarifies extent.
When tendon repair becomes necessary
Not all tendon injuries require repair. Minor strains often heal conservatively. Complete tears disrupt function significantly. Persistent weakness suggests structural damage. As a result of our editor’s research, repair is considered when natural healing fails. Decision balances function and risk. Individual needs guide timing.
What tendon repair aims to achieve
Repair restores continuity between muscle and bone. It seeks to reestablish tension and alignment. Strength recovery follows structural healing. According to our editor’s reviews, repair success depends on healing environment. Surgery addresses structure, not strength alone. Rehabilitation completes the process.
How imaging supports diagnosis
Imaging clarifies injury details. Ultrasound shows tendon continuity. MRI reveals tear size and quality. Imaging guides treatment decisions. As a result of our editor’s observations, accurate diagnosis prevents overtreatment. Visual evidence informs expectations. Precision improves planning.
Why timing matters in repair
Early repair prevents retraction and degeneration. Delayed repair complicates alignment. Tissue quality declines with time. According to our editor’s research, earlier intervention improves outcomes. However, swelling must settle first. Balance determines optimal timing.
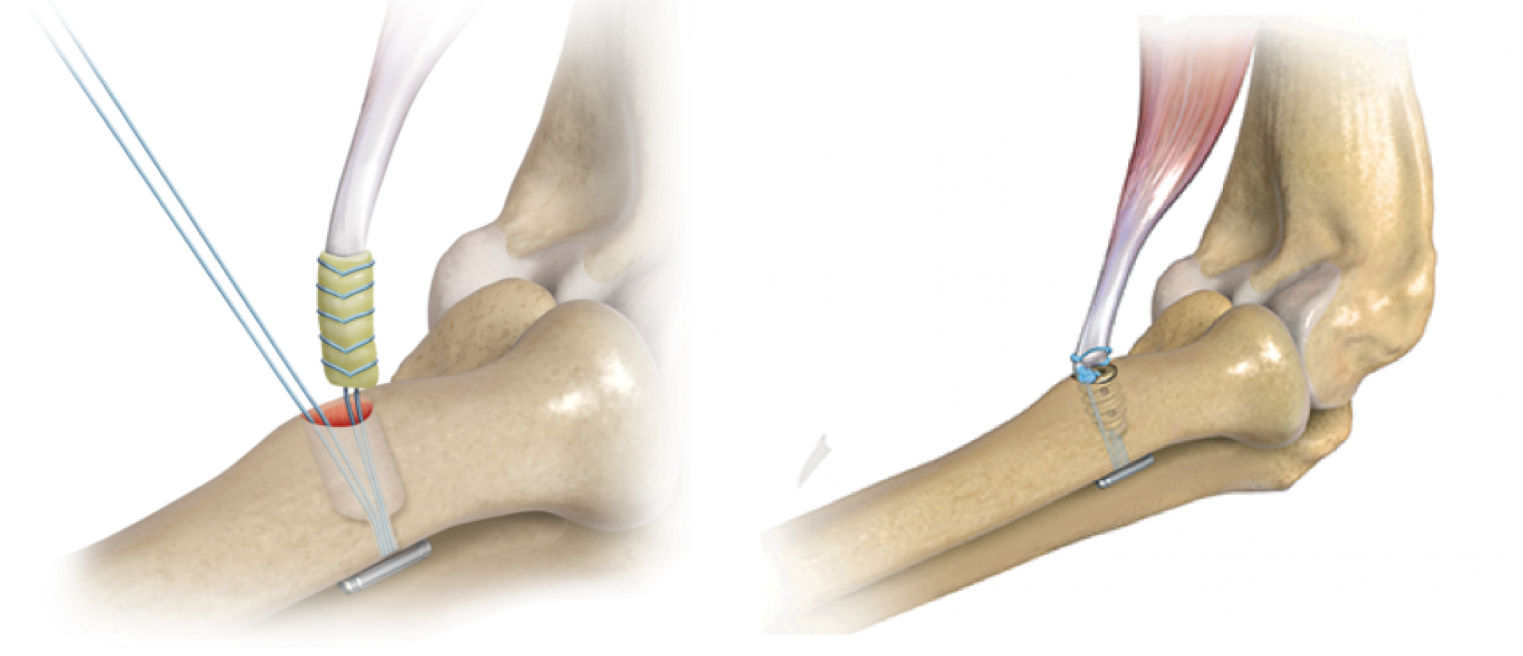
What surgical repair involves
Surgical repair reconnects torn tendon ends. Techniques vary by tendon location. Sutures anchor tissue securely. Sometimes anchors attach tendon to bone. As a result of our editor’s reviews, modern techniques improve strength. Precision reduces retear risk. Surgery remains one step.
How minimally invasive approaches help
Some repairs use smaller incisions. Minimally invasive techniques reduce tissue disruption. Recovery may feel smoother initially. According to our editor’s observations, approach depends on injury type. Not all tendons suit minimal access. Surgeon expertise guides choice.
What happens immediately after repair
Immobilization protects the repair initially. Movement restrictions prevent stress. Pain and swelling are expected. According to our editor’s research, early protection is critical. Premature motion risks failure. Patience supports healing.
Why rehabilitation is essential
Rehabilitation restores strength and flexibility gradually. Tendons adapt slowly to load. Guided exercises rebuild tolerance. As a result of our editor’s reviews, rehab determines long term success. Surgery alone cannot restore function. Consistency matters.
How healing progresses over time
Tendon healing occurs in phases. Initial inflammation stabilizes repair. Collagen fibers reorganize gradually. Strength increases slowly. According to our editor’s observations, full healing takes months. Rushing delays progress. Time supports durability.
What limits early movement
Early movement risks stretching repair. Tendons need time to anchor. Excess motion weakens sutures. As a result of our editor’s research, controlled motion replaces rest later. Phases matter more than speed. Structure precedes strength.
How pain should be interpreted
Pain does not always indicate damage. Healing tissues remain sensitive. Sharp pain requires attention. Dull discomfort may be normal. According to our editor’s reviews, communication guides adjustments. Listening prevents setbacks. Balance remains key.
Why strength returns gradually
Muscles weaken during immobilization. Tendons regain stiffness slowly. Coordination rebuilds with practice. As a result of our editor’s observations, gradual loading protects repair. Progress feels uneven. Persistence pays off.
What risks exist with tendon repair
Risks include stiffness, retear, or infection. Scar tissue may limit motion. Adherence reduces complications. According to our editor’s research, risk remains low with guidance. Understanding sets realistic expectations. Awareness improves compliance.
How age affects tendon healing
Healing slows slightly with age. Tendon elasticity decreases naturally. Blood supply changes over time. As a result of our editor’s reviews, age influences pacing, not success. Older adults still recover well. Adaptation matters.
Why tendon location matters
Different tendons experience different loads. Weight bearing tendons face higher stress. Hand tendons require fine control. According to our editor’s observations, location shapes repair strategy. Rehabilitation adapts accordingly. Function guides goals.
How nutrition supports recovery
Protein supports tissue repair. Vitamins aid collagen formation. Hydration affects tissue quality. As a result of our editor’s research, nutrition influences healing environment. Balanced intake supports progress. Recovery extends beyond therapy.
What role rest plays
Rest protects healing structures. Sleep supports tissue repair hormones. Overactivity delays recovery. According to our editor’s reviews, rest complements exercise. Both matter equally. Balance sustains healing.
How expectations shape recovery
Realistic expectations reduce frustration. Progress appears gradual. Plateaus are common. As a result of our editor’s observations, mindset influences adherence. Patience supports persistence. Trust the process.
Why follow up appointments matter
Follow ups monitor healing progress. Adjustments optimize rehabilitation. Imaging may confirm stability. According to our editor’s research, monitoring prevents complications. Communication keeps recovery aligned. Guidance evolves over time.
How daily activities are reintroduced
Activities return gradually. Light tasks precede heavy loads. Function improves stepwise. As a result of our editor’s reviews, pacing protects repair. Small gains accumulate. Everyday confidence returns.
What signs require attention
Sudden pain increase warrants evaluation. Swelling or redness may signal issues. Loss of function needs review. According to our editor’s observations, early reporting prevents setbacks. Awareness supports safety. Do not ignore changes.
Why adherence matters more than intensity
Consistency outweighs aggressive effort. Skipping steps weakens outcomes. Structured plans guide progress. As a result of our editor’s research, adherence predicts success. Discipline supports durability. Trust guidance.
How tendon repair affects long term function
Most regain strong function. Some stiffness may persist. Adaptation compensates for minor limits. According to our editor’s reviews, outcomes remain positive. Repair restores confidence. Movement feels reliable again.
What tendon repair does not guarantee
Repair does not prevent future injury automatically. Conditioning remains necessary. Awareness supports prevention. As a result of our editor’s observations, maintenance matters. Strength and flexibility protect gains. Responsibility continues.
How prevention fits after repair
Warm up reduces strain. Gradual loading protects tendons. Technique matters in activity. According to our editor’s research, prevention preserves repair. Habits shape longevity. Care continues beyond healing.
Why understanding repair matters
Knowledge reduces fear and confusion. Clear expectations support engagement. Recovery feels manageable. As a result of our editor’s reviews, informed patients adhere better. Understanding empowers participation. Confidence grows with clarity.
How recovery becomes personal
Every repair differs slightly. Goals vary by lifestyle. Progress adapts individually. According to our editor’s observations, personalization improves satisfaction. One plan does not fit all. Collaboration guides success.